Pakistan proudly became the first country to volunteer for the Digital FDI Initiative, paving the way for the launch of Digital FDI-Enabling Projects (DEPs) in 2022. This initiative is designed to enhance digital foreign direct investment in Pakistan by fostering a supportive, digital-friendly investment environment.
The project seeks to attract investors and stimulate activity, offering opportunities:
- To access advanced technologies
- Global Expertise
- Robust infrastructure.
These investments have the potential to boost resilience, boost competitiveness, and quicken economic growth. This report analyses Pakistan’s digital economy using the Digital FDI framework illustrated in Figure 1.
Project activities
Pakistan’s Digital FDI-Enabling Project (DEP), which aims to expand its portfolio of digital FDI, fits in perfectly with its larger digital transformation goal. The initiative aims to identify and eliminate growth impediments while revealing the potential to improve foreign direct investment in Pakistan’s digital economy through collaboration with key stakeholders and analysis of the digital landscape. The structured approach includes the following activities:
Initial Engagements
Conducted introductory meetings to align project objectives with the Government of Pakistan counterparts.
Performed a desk review to evaluate:
- Policy and regulatory frameworks.
- Trends and developments in FDI, technology, and investment landscapes.
- Key stakeholders and factors influencing digital FDI in Pakistan.
Stakeholder Consultations
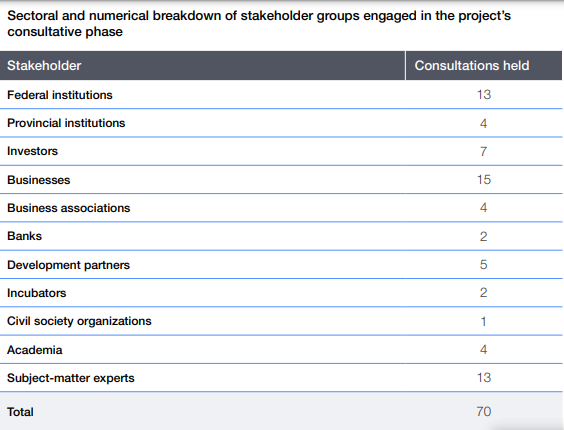
- Organized a comprehensive consultative exercise with 70 key stakeholders, including local and international entities.
- Held 65 in-person consultations in Islamabad, Lahore, and Karachi, supplemented by five virtual sessions.
- Engaged a diverse group of stakeholders across the digital ecosystem, as detailed below.
This structured approach ensures a thorough understanding of Pakistan’s digital investment landscape and fosters informed decision-making to attract and grow digital FDI.

Six Priority Actions
1. Promote Sectoral Projects
Facilitate private-sector initiatives based on sector priorities and ticket size to connect local players with international investors and partners.
2. Prime Minister’s Office Role
Strengthen the PM’s Office’s involvement in implementing digital economy priorities and boosting investor confidence through a better enabling environment.
3. Human Capital Development
Bridge the industry-academia gap to enhance digital skill sets through advanced education and internationally accredited training programs.
4. Investment-Friendly Policies
Offer a rationalized and stable tax policy and regulatory framework to position Pakistan as a digital-centric investment destination.
5. Special Technology Zones (STZs)
Expedite the operationalization of STZs to attract global investors and technology players.
6. Efficient Spectrum Management
Ensure fair pricing and transparent processes for spectrum management, enabling timely network deployment and improved connectivity.
This structured approach sets a strong foundation for implementing actionable reforms to advance Pakistan’s digital FDI growth.
Pakistan’s digital ecosystem
To promote foreign direct investment (FDI) in the digital ecosystem, Pakistan launched the Digital Economy Project (DEP) to identify the factors that drive, hinder, and present opportunities for intervention. This multi-stage process involved extensive consultations with key stakeholders, combining in-country and virtual inputs to create actionable insights.
Digital FDI Framework
The project leverages the Forum’s Digital FDI framework to develop Pakistan’s digital economy. Analysis of the current digital landscape is categorized under relevant pillars to identify stakeholders, challenges, and opportunities for FDI. While each pillar is distinct, they often overlap when applied to Pakistan’s dynamic digital ecosystem.
Defining the Digital Economy in Pakistan
Pakistan lacks a formal definition for the “digital economy,” and no standalone metrics are assigned to it in official datasets. Consequently, the analysis relies on indicators from identifiable digital segments and FDI trends.
Read More: SDF to Invest $100M in Pakistan’s Mineral Infrastructure Growth
Key Stakeholders and Engagement Activities
Pakistan’s digital economy involves a complex network of stakeholders operating at federal, provincial, and sectoral levels. The DEP team actively engaged these stakeholders to gather insights and inform project outcomes.
Activities included
- Stakeholder Mapping: Categorized key players influencing and governing the digital economy (see Annex for details).
- Consultations: Conducted multiple in-country and virtual engagements.
- Follow-Up Meetings: Ensured clarity and alignment on objectives.
- Workshops: Hosted a dedicated session for stakeholders to share perspectives and align on outcomes.

Mapping Pakistan’s Digital Economy
The DEP analyzed the country’s digital ecosystem through consultations, surveys, and research. Key findings are organized as follows:
1. Digital Infrastructure
Physical Infrastructure
- Broadband Expansion: 91% population coverage, with 3G/4G accessible to 81%.
- Subscriber Growth: 142.3 million broadband users in 2024 (91% growth since 2019).
- Mobile-First Landscape: 79.1% mobile phone ownership, with 65% being smartphones.
- Fixed Broadband Penetration: Less than 2%, marked as a priority for development.
Regulatory Infrastructure
- Initiatives such as PRMI and Special Technology Zones (STZs) aim to streamline processes and attract digital FDI.
- Enhanced coordination between federal and provincial agencies is required to minimize regulatory fragmentation.
- Critical legislation, including the Personal Data Protection Bill, needs finalization to strengthen the investment climate.
2. Digital Adoption
- The Digital Pakistan Policy (2018) spurred digital growth in sectors like banking, education, and health, but SMEs face adoption barriers due to low digital literacy and limited access to tools.
- Post-pandemic digital acceleration needs sustained support through macroeconomic stability and regulatory consistency.
3. New Digital Activities
- Cloud Computing: Local sponsors dominate data centers, with international players like AWS and AliCloud entering through partnerships.
- Social Media Platforms: Platforms like Google have established liaison offices, while others maintain virtual presences due to data protection challenges.
- Data Localization: Strengthening data protection laws and enforcing intellectual property regulations are critical for attracting hyperscalers and ensuring investment security.
4. Digital Services Exports and Outward FDI
- IT Exports: Reached $3.2 billion in 2024, reflecting a 24% year-on-year growth.
- Regional Comparison: Despite progress, Pakistan lags behind regional peers, highlighting the need for supportive ecosystems for outward FDI.
Read More: The Imperative of Social Protection for Gig Workers in the Digital Economy
Recommendations for Strengthening Digital FDI
To enhance FDI in Pakistan’s digital economy, the following recommendations have been prioritized:
- Develop a Unified Digital Governance Framework: Foster coordination between federal and provincial agencies to streamline regulatory processes.
- Strengthen Data Protection Laws: Finalize the Personal Data Protection Bill and enforce intellectual property protections.
- Support Digital Infrastructure Growth: Focus on expanding broadband, operationalizing STZs, and ensuring fair spectrum pricing.
- Enhance Digital Literacy: Bridge gaps through advanced education and internationally accredited training programs.
- Simplify Bureaucratic Processes: Expedite document handling, dispute resolution, and arbitration to improve investor confidence.
These strategies aim to position Pakistan as a competitive destination for digital FDI and foster long-term growth in the digital economy.
This streamlined version integrates clear headings and bullet points for better readability while maintaining a professional tone. Let me know if further adjustments are needed!
Digital FDI in Pakistan
Pakistan has garnered relatively modest levels of digital Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), especially when compared to regional counterparts like:
- India
- Indonesia.
For context, FDI in India is approximately 20 times higher.
Figures 3, 4, and 5 provide a five-year overview of digital FDI trends in three key sectors:
- IT
- Telecommunications
- Start-ups.
Read More: First Digital Bank in Pakistan: Banking Anytime, Anywhere
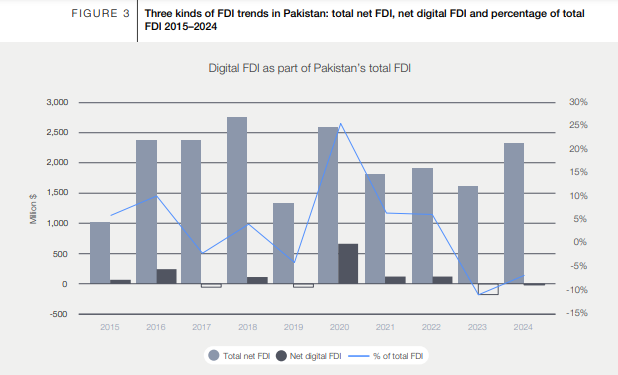
Between 2018 and 2024, Pakistan experienced some growth in net digital FDI, though fluctuations were evident, with net FDI turning negative in 2023 and 2024. This shift indicates higher outflows than inflows. A eminent spike in digital FDI happened in 2020, fueled by investments amid the COVID-19 widespread, but this force has since diminished.
In FY 2022, the IT and telecom divisions together accounted for 6% of Pakistan’s add-up to FDI, a critical drop from 25% in FY 2020. The later decay in digital FDI is credited to challenging nearby and worldwide macroeconomic conditions, counting instability in the Pakistani rupee (PKR) against the US dollar.
The formation of a modern government in February 2024 presents an opportunity to stabilize political conditions, modify investor certainty, and draw in renewed digital FDI.

Historically, Pakistan’s telecom sector led digital FDI inflows, but in FY 2022, it recorded a net outflow of $29 million due to taxation, spectrum pricing, and currency fluctuations. With spectrum prices tied to the US dollar, telecom operators face challenges in fulfilling payment obligations.
Changes are required to ease financial pressures and make the division more investment-friendly.
Growth openings include the upcoming 5G spectrum auction, MVNO approach, versatile gadget fabricating activities, and the National Fiberization Policy, which points to extending high-speed internet. Additionally, the National Space Policy 2023 could enhance connectivity and technological advancements.
Start-ups have emerged as key drivers of digital FDI, attracting $355 million in 2022, primarily in fintech, edtech, and agritech. However, investments dropped to $37 million by late 2024. Deals like DigitalOcean’s $350 million acquisition of Cloudways highlight the potential of technologies like blockchain and IoT to reshape Pakistan’s digital economy. Strategic support could revive growth and strengthen the sector.














